New PROLAN ELPULT CTC in Fonyód
Wednesday morning, the new central traffic control system (DBV Köfi) of the Southern Railway line was handed over. The essence of the Köfi system is that the traffic of that line segment is not directed at individual stations, but from a single service center.
The headquarters of DBV CTC is Fonyód, and fifteen of the 21 stations in the 144 km distance from Szabadbattyán to Nagykanizsa have been remote control. In Fonyód, Szabadbattyán, Lepsény, Siofok, Balatonszentgyorgy and Nagykanizsa only a CTS system has been built, here the safety equipment is still handled locally. The other stations' transmissions and signals are remotely controlled from the Fonyod center.
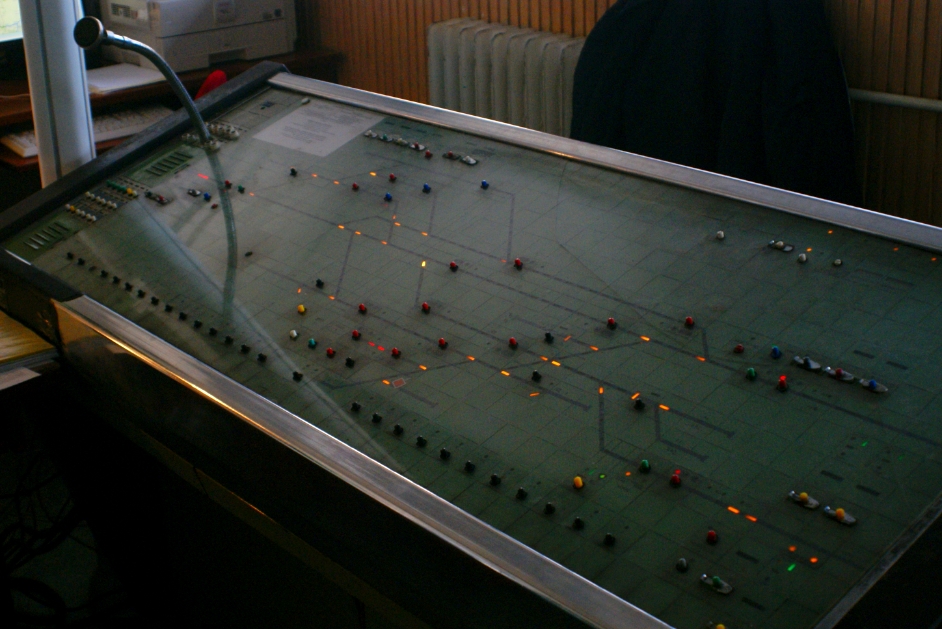
Old CTC, which was eighteen years ago, only covered the line from Szabadbattyán to Balatonszentgyörgy. Though the system was the highest technical standard at that time, then the official regulations required the presence of a so-called presence traffic service station at the remote stations. His task was primarily "presence", but he had to intervene only in certain malfunctions that could not be managed by the center. With the rapid development of technology this time has passed, so it is necessary to build a new, advanced computer-controlled routing system that provides the highest possible security level and does not require the presence of a traffic worker at the stations. The launch of the new Köphy will not bring down dismissals. Most of the rail passengers concerned moved to the Fonyod center in a similar position to the previous one, moving others to other stations. There were those who used the option of early retirement, and there were rail passengers who served on a railroad job in other positions, such as a personal trainer or as a caretaker of unattended buildings.
A major advantage of central traffic management is that traffic managers can review the traffic of the entire line so that with a system-wide decision they can reduce train queues and their impact, thus improving the line's timing. The CTC Center in Szeged has been operating since 2009, since then the scheduled and connected rail lines have been running far beyond ninety percent, around 97-98 percent. During the summer scheduling period, 140 to 150 train journeys are running on the Southern Railway line, which is very significant. On a one-lane section, the delays of a train and a bad decision on the spot may even have hours in the afternoon. This will largely change the central management, where trained railway workers can take decisions with the slightest delay, taking into account the current position of the entire line section, the location of the trains and the technical state of the equipment.
Remote hosted stations are left unattended, so it may be that in case of a small, local technical failure, troubleshooting will take more time and confusion will increase. Thanks to the central control, however, all train loses will still decrease.
The system that was completed in the general construction of Prolan did not change or rebuild the local security equipment of the stations. Thus, for example, at the Fonyód station, which is located at the Köfi Center, the hand-operated tensile barrier has remained to this day. The same Domino systems with relay equipment continue to serve the stations. Each station is connected to each other by Prolan's unique development, the Elpult electronic board, an interface that delivers digital signals from the CTC Center computer to the station security device. The company has extensive experience in the construction of similar systems, and has carried out similar work several times before ordering the MÁV. This is also due to the fact that the work was carried out without a disturbance of rail traffic in just 510 days, in a timely and high quality manner.
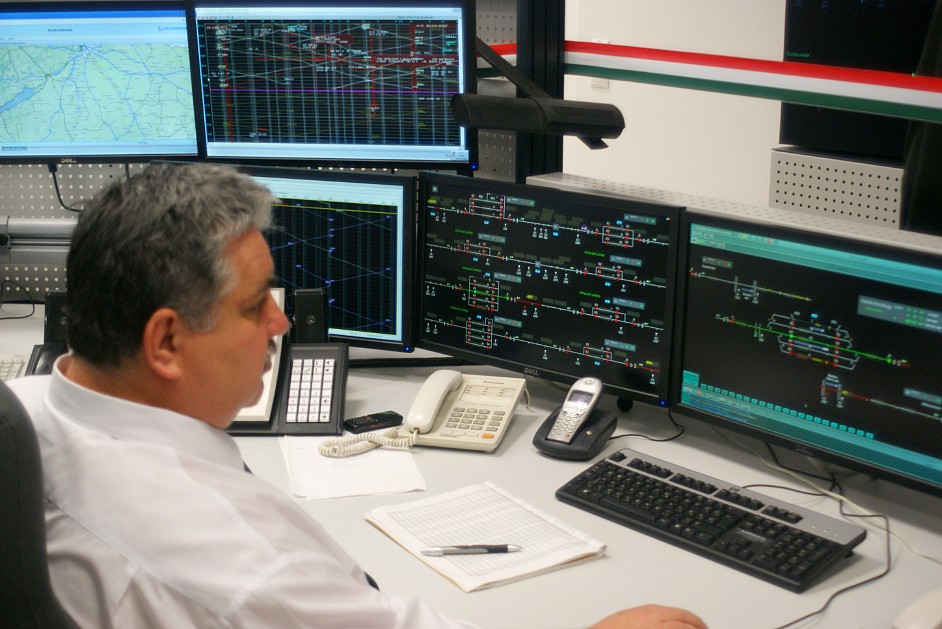
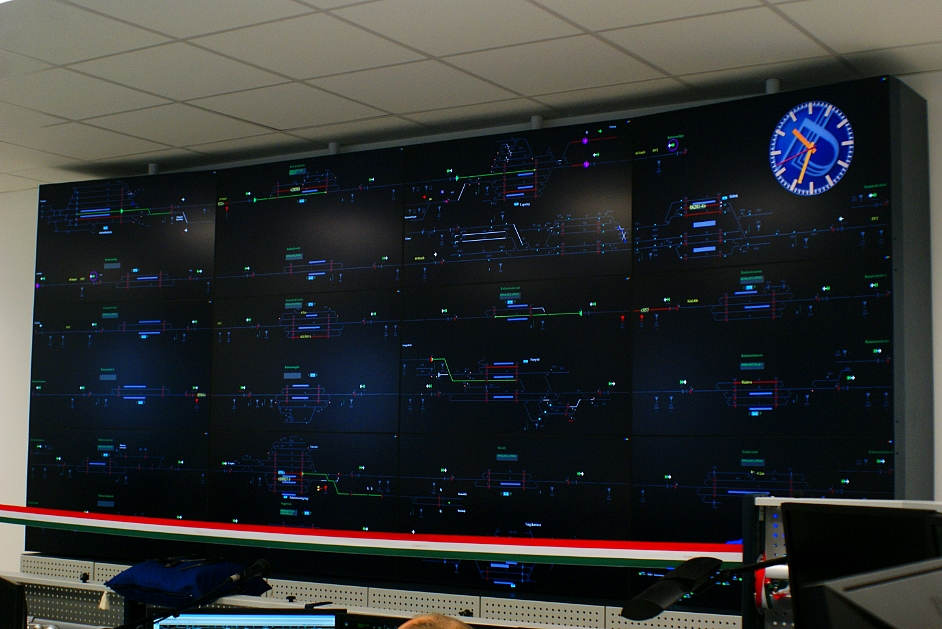
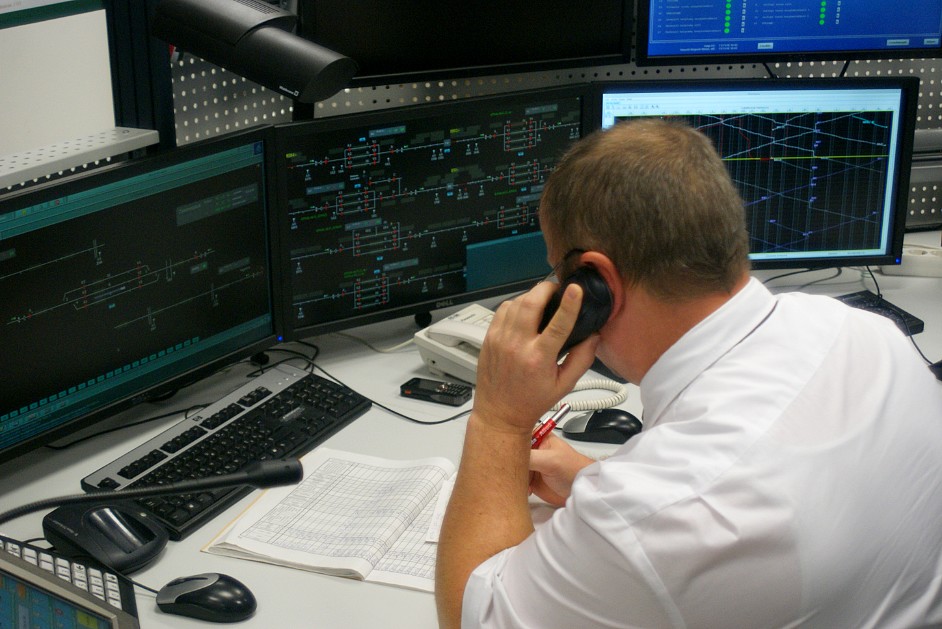
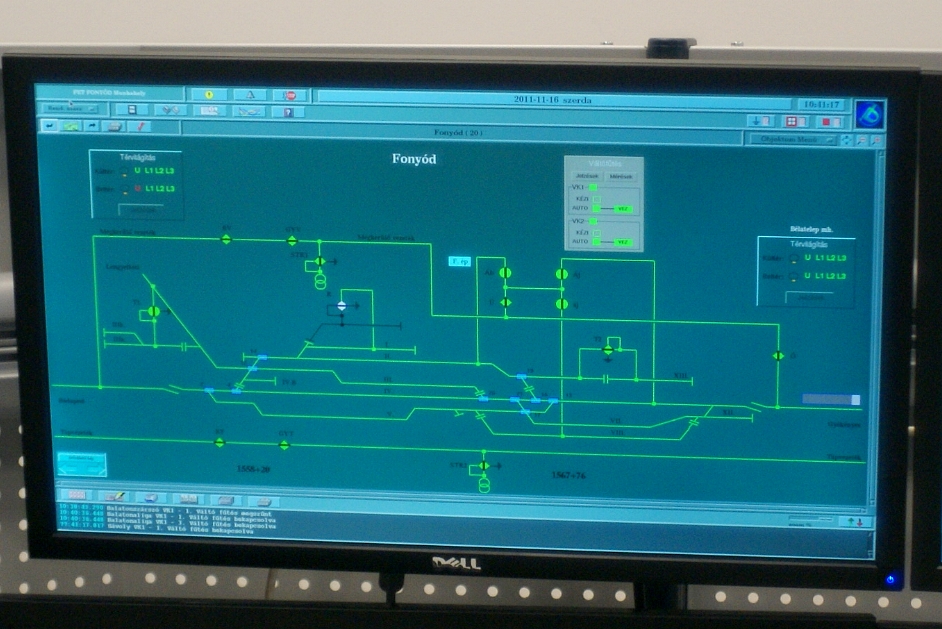
At the Fonyod center, the railway station line from Szabadbattyán to Nagykanizsa, the current status of all stations and their equipment, switches, signalers, road transitions, the location of the trains on a 12-screen monitor wall, and individual workers on their own monitors. There are usually three people in the center at the same time. Two routers direct the trains to the two halves of the line and their work is controlled by a driver. The fourth workstation is a reserve, and in case of failure, it can take the role of both the router and the router workstation.
The routers work is supported by automatic programs. The computer must only tell whether the train is simply passing through or crossing another train and the system will automatically perform the necessary operations. Sets the track, closes the barriers if it needs and handles flags for arriving trains.
The power supply and feeding of the electric overhead line of the line section can also be controlled from the Fonyod center. The Catenary Remote Control (FET) received a separate screen as well as a transceiver monitoring monitor. From Lake Balaton and its surroundings, many of us have a pleasant warm, sunny summer weather, but this is not always the case. Winter cold, built-in and cracked snow can make it harder, sometimes it may stop the shifting of barges. To prevent this from happening and to make the changeover from the Fonyod center always safely, all the stations on the line have been installed and the existing ones have been refurbished. The power supply of the alternator equipment is effected through the overhead contact line by means of column transformers.
Automatic, train-driven loud and visual visual information systems were built at the remote stations and stops. Arrival of the fittings and possible delays will be automatically warned on the basis of information from your Köfi computer. Of course, routers in the center can manually intervene in the system at any time. Some stations have experimentally set up touch-sensitive information columns where the passenger can find minute-accurate timing information from the Köfi system. Automatic, train-driven loud and visual visual information systems were built at the remote stations and stops. Arrival of the fittings and possible delays will be automatically warned on the basis of information from your Köfi computer. Of course, routers in the center can manually intervene in the system at any time. Some stations have experimentally set up touch-sensitive information columns where the passenger can find minute-accurate timing information from the CTC system.
In order to reduce energy consumption, the "depopulation", ie without railroad workers, and street stops, automated street lighting. Before the train arrives, the lights are switched on the platform so the passenger must not climb the stairs of the train wagon in the dark. After the passing of the fitting, the lighting became a savings operation to avoid unnecessarily consuming electricity.
In remote stations, security, alarm and fire protection systems were built. In addition to motion detectors equipped with buildings, the doors are equipped with a twin-chip electric lock and the windows are equipped with an ultrasonic burglar detector. Probably this will not happen here that happened a few days ago at the railway station in Sárosvár.
The total value of the project was nearly two and a half billion forints, and funding was implemented in a special construction. Prolan Zrt., The general contractor, is responsible for the cost of the construction, and the railway company pays the contractually stipulated amount of the savings due to the system.
In addition to building several smaller routing systems, a major investment is included in the plans. If the financing structure is born, within two or three years the central traffic control system, including the section between Szabadbattyán and Tapolca, can be completed on the north coast.
2011.11.17